With the rapid development of mining technology, the automation level of mining machinery and equipment is also continuously improving. Ore transportation is a key link in mining. The reasonable selection and safe maintenance of transportation equipment are of great significance to improving the economic benefits of enterprises and ensuring safe and efficient transportation in mining.
The port belt conveyor is a device used for loading and unloading ore at the port. It unloads and unloads ore from cargo ships when going down and loads ore onto cargo ships when going up. It is generally composed of conveyor belts, racks, drives, tensioners, brakes, belt storage, cleaning and other devices. The traditional port belt conveyor uses a frequency converter to drive an asynchronous motor, which has the disadvantages of poor drive stability, low transmission efficiency, unbalanced master-slave power distribution, and high energy consumption. With the rapid development of permanent magnet direct drive technology and frequency conversion technology, ore transportation solutions are more efficient, have lower power consumption, better reliability, longer transmission distances, and stronger multi-machine master-slave synchronization performance. This article introduces the application of INVT GD350A series VFD to balance power in permanent magnet direct drive on port belt conveyor equipment.
Customer requirements
The belt conveyor equipment at a port in Guangdong mainly transports iron ore, with a transport capacity of 6000T/h, a maximum cargo capacity of 8000T/h, a transport length of 1430m, a transport inclination of 0-5°, a lifting height of 5.78m, a belt width of 1800mm, a maximum belt speed of 3.14m/S, and a drive roller diameter of 1000mm.
1. Multi-VFDs power balance: Two motors are equipped with the same set of belts, and real-time power balance must be strictly guaranteed to avoid motor pulling due to speed asynchrony, which will increase internal losses and VFD failures.
2. High torque at low speed: The belt needs to start and stop at will, and it is necessary to ensure the synchronous output of high torque during full-load startup and balanced power distribution during acceleration and deceleration stages.
3. Low-speed permanent magnet motor direct drive: Excellent high-power permanent magnet motor driving performance, ensuring vector control performance under extremely low speed/high power permanent magnet synchronous motor.
4. Long-distance signal transmission stability: The two VFDs are far apart, and it is necessary to ensure stable transmission of communication signals and control signals over long distances.
5. High-power frequency conversion drive: Ultra-high-power low-voltage frequency converters often use a multi-machine cabinet solution, and the reliability and stability of the multi-machine cabinet solution must be ensured.
INVT Solution
The two permanent magnet direct-drive motors use INVT GD350A-1000G-6 VFD respectively. The two VFDs use open-loop vector control to ensure high torque output under full-load startup. Considering that the two VFDs need real-time power distribution balance, the two VFDs are synchronized with each other, and real-time data interaction is performed by adding CAN master-slave cards. The master and slave VFD each add a certain amount of droop for power balance adjustment.
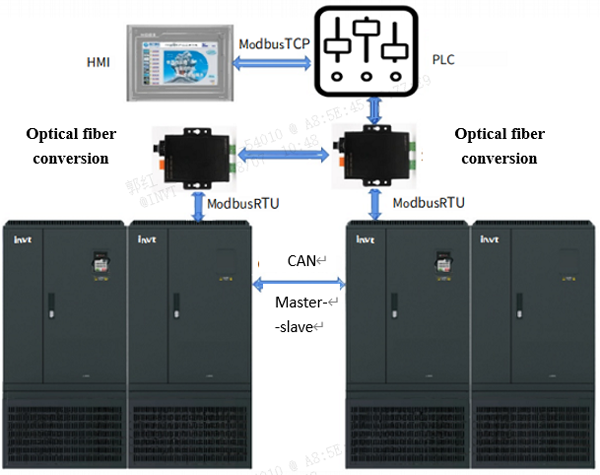
Master-slave power balance: Two VFDs, one master and one slave, the master receives the given frequency sent by the PLC, writes the current running frequency to the slave through the CAN master-slave card, and reads the running frequency and output torque of the slave. The master-slave VFD adds the droop frequency on the basis of the given frequency, and finally ensures that the master and slave can quickly adjust the running frequency and ensure the dynamic balance of the master and slave power.
Low-speed and high-torque starting: Both the two VFDs use a dedicated SVC control solution for permanent magnet direct-drive motors, with excellent output performance at low-speed direct drive, ensuring load starting and power balance control performance under full load conditions.
Long-distance signal transmission: The distance between the two VFD is 1,400m. Modbus communication and CAN master-slave communication are respectively equipped with optical fiber conversion modules to ensure the reliability of long-distance signal communication transmission.
High-power VFD: The maximum power of a single 380VAC level GD350A series VFD is 630kw. If it exceeds 630kw, a parallel solution is required. In this solution, the GD350A-1000G-6 VFD uses two 500kw VFD in parallel. The parallel board sends the master-slave drive signal through optical fiber to ensure the synchronization of the drive signal. The parallel VFDs are equipped with input and output reactors to ensure balanced distribution of the current.
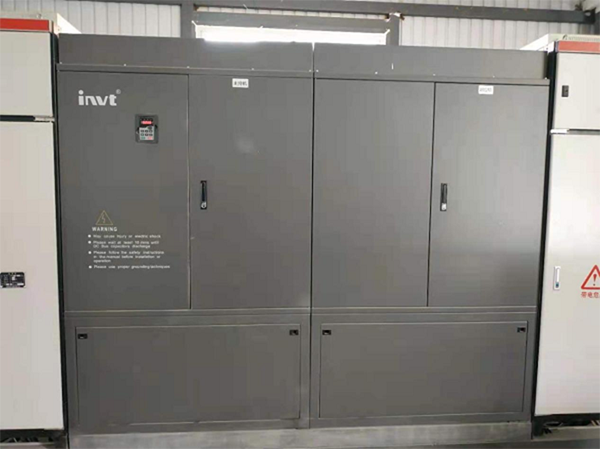
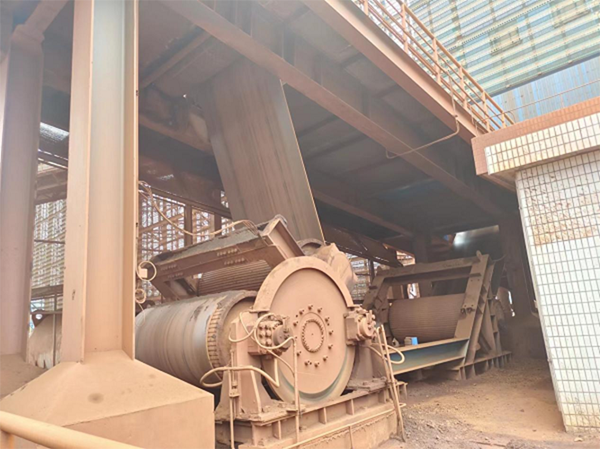


Master-slave control is a common control model in automation systems. Due to the diversity of load types, there is no clear model for the control solution, but it needs to be adapted according to the load type and control requirements. This solution is a mature solution of INVT in port belt conveyor applications due to its high motor power, long distance between master and slave motors, large direct drive torque, and high drive control difficulty. Its excellent product performance has been highly recognized by customers.

Our site uses cookies to provide you with a better onsite experience. By continuing to browse the site you are agreeing to our use of cookies in accordance with our Cookie Policy.